1.5. How AI Learns: The Core Mechanisms
Hou I (Esther) Lau
In this chapter, we now move under the hood of AI to examine the mechanics of how machines learn. Neural networks, natural language processing (NLP), and large language models (LLMs) are the engines that allow modern systems to generate convincing outputs. By understanding these components, we can better judge what AI can and cannot do.
Neural Networks: Brains Made of Math
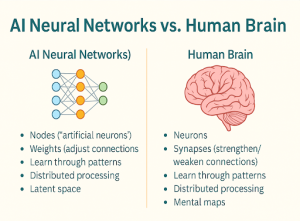
Neural networks are inspired by the structure of human brains, but they are not biological; they are mathematical models made of layers of nodes, or “artificial neurons.”
- Nodes: units where data flows and decisions are made.
- Weights: adjustable strengths of the connections between nodes, tuned during training.
- Patterns: the system improves by refining which connections lead to accurate outcomes.
- Distributed processing: information is represented across the network, not stored in a single place.
- Latent space: abstract internal representations where models capture relationships we did not explicitly teach them.
📖 Analogy: Trails in a Forest
Think of learning as carving trails. In human learning, the “trail” is not just a path in the brain. It carries meaning, emotion, and context from lived experience. In machine learning, the trail is a strengthened mathematical pathway through a network: connections (weights) get adjusted so the system follows routes that reduce error. Both create paths, but only one is anchored in experience and meaning.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
How do machines work with human language? This is the domain of NLP. NLP enables machines to parse, generate, and manipulate language. It does not mean the system understands in a human sense. Instead, it encodes, stores, and retrieves patterns in text.
- Encoding: words are converted into data (tokens).
- Storing: tokens are embedded in vectors that capture statistical relationships.
- Retrieving: models generate new text by predicting the most likely next word given surrounding context.
For example, in the sentence: “The therapist sat with the couple during their …”, a human supplies “session” based on context. An AI model does the same statistically, scanning nearby words to predict the most probable continuation.
Large Language Models (LLMs)
LLMs scale NLP with deep learning. They are trained on enormous corpuses of textual datasets comprising books, articles, websites, and conversations and capture the rhythms and structures of human language. They are not memorizing, but predicting patterns at scale.
Capabilities:
- Generate essays, summaries, and explanations.
- Classify or translate text.
- Brainstorm, code, or mimic tone and style.
LLMs produce fluent, human-like responses, but remember: they do not understand in human terms. They excel at pattern prediction, not meaning.
From LLMs to GPT
One of the most well-known LLM architectures is GPT, or Generative Pre-trained Transformer.
- Generative (G): produces original text—stories, summaries, answers, even code.
- Pre-trained (P): trained on massive datasets before being fine-tuned for tasks.
- Transformer (T): a neural network design that captures long-range context and relationships in text.
GPT models respond to prompts, such as questions, commands, fragments, by predicting what comes next based on everything they have seen in training. If LLMs are the brain, GPT is the conversational voice.
📚 Weekly Reflection Journal
How does the concept of “latent space” in AI compare with your own experiences of intuition or “gut feelings”? Write a short note reflecting on whether the metaphor feels accurate or misleading.
More on Neural Networks
Click through the labeled hotspots to see how data moves through an AI model.
Quick Self-Check
Test your understanding of NLP and LLMs by filling in the missing terms.
Looking Ahead
Next, we turn to a human-centered approach to AI: how educators and professionals can frame these technologies in ways that serve human learning and flourishing.
